Plastic molding techniques are foundational to the manufacturing industry, enabling the production of countless everyday items, from water bottles to car parts. Two of the most commonly used methods are blow molding and injection molding. While both techniques are essential, they differ in process, materials, applications, and product outcomes. Let's dive into what sets these two molding methods apart and when each one shines.
What is Plastic Molding?
Plastic molding is a manufacturing process used to shape plastic into a wide variety of forms. This technique involves melting plastic materials and injecting, blowing, or extruding them into molds to produce objects in desired shapes and sizes. It’s a process that allows mass production of plastic parts, contributing to industries like automotive, healthcare, and consumer goods.
Why is Plastic Molding Essential in Manufacturing?
From small components like bottle caps to large items like car bumpers, plastic molding ensures efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and precision in producing multiple copies of an item. By allowing for a high degree of customization, it also meets specific industry requirements, leading to vast applications in various sectors.
Definition of Blow Molding
Blow molding is a plastic molding process primarily used to produce hollow objects. The process involves blowing air into melted plastic inside a mold to form the plastic into the shape of the mold, similar to how glass blowing works. This technique is ideal for creating bottles, containers, and other hollow shapes.
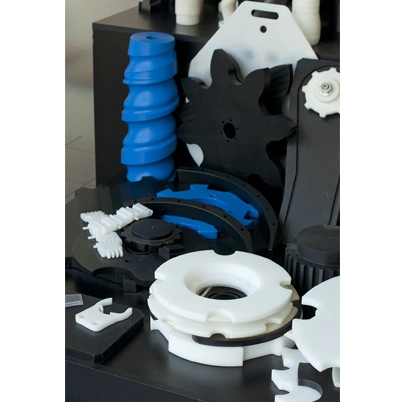

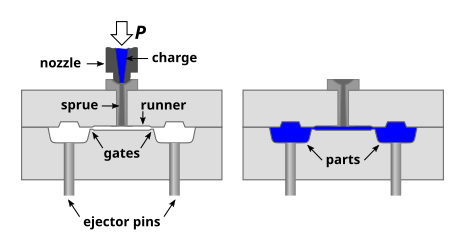
Definition of Injection Molding
Injection molding, on the other hand, is used to create solid parts. In this method, melted plastic is injected into a mold at high pressure and cooled to form a solid shape. This process is widely used to produce everything from small components to larger parts like dashboards or medical equipment.
Wikipedia
How Blow Molding Works
Blow molding begins with melting down plastic and forming it into a parison (a tube-like shape with a hole in one end). The parison is placed inside a mold, and air is blown into it, forcing the plastic to expand and take the shape of the mold. Once it cools, the mold is removed, and the hollow plastic object is complete.
How Injection Molding Works
In injection molding, the plastic is melted and injected into a mold cavity under high pressure. The mold is typically made of metal and is split into two halves. After the plastic fills the mold cavity and cools, the two halves separate to release the solidified part. Injection molding allows for the creation of highly detailed and complex parts.
Materials Commonly Used in Blow Molding
Blow molding uses lightweight, flexible plastics that can withstand the inflation process without tearing. Common materials include polyethylene (PE), polypropylene (PP), and polyvinyl chloride (PVC), which are suitable for creating hollow products like bottles.
Materials Commonly Used in Injection Molding
Injection molding requires materials that can withstand high pressures and still produce fine details. Common materials include ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene), polystyrene (PS), and nylon, which are ideal for creating strong, detailed, and durable parts.
Types of Products Created with Blow Molding
Blow molding services are commonly used for items that need a hollow structure, such as beverage bottles, fuel tanks, plastic containers, and blow molded automotive parts. It’s perfect for lightweight and thin-walled items.

Types of Products Created with Injection Molding
Injection molding produces solid items and parts with complex shapes and intricate details. Typical products include electronics casings, medical devices, toys, and automotive plastic injection molding. The versatility of injection molding makes it suitable for a wide range of items with high structural integrity.
Advantages of Blow Molding
Efficient for High Volumes: Blow molding is ideal for mass production of hollow parts, leading to faster production times and lower costs per unit.
Lightweight Products: Blow-molded items are typically lighter than injection-molded parts, making them useful for packaging.
Economical for Simple Shapes: Blow molding works well for products with simple shapes, as it requires fewer materials and energy.
Disadvantages of Blow Molding
Limited to Hollow Products: Blow molding is limited to creating hollow objects, so it’s not suitable for solid or highly detailed parts.
Lower Precision: The blow molding process doesn’t allow for high precision, so parts may have less detail compared to injection molding.
Advantages of Injection Molding
High Precision and Detail: Injection molding allows for intricate designs and highly detailed parts, making it ideal for complex shapes.
Durable and Strong Products: Injection-molded items are robust and can withstand heavy-duty use.
Versatility: Injection molding is suitable for a wide range of shapes and sizes, from tiny components to large structural parts.
Disadvantages of Injection Molding
Higher Costs for Small Runs: Due to tooling expenses, injection molding can be costly for small production runs.
Longer Setup Time: The process requires more setup time, which can delay production compared to blow molding for certain projects.
Automotive Industry
Both blow molding and injection molding play essential roles in the automotive industry. Blow molding produces fuel tanks and fluid reservoirs, while injection molding creates dashboards, door panels, and various under-the-hood components.
Packaging Industry
Blow molding is widely used in packaging, especially for creating lightweight and hollow containers like bottles for beverages and cleaning products. Injection molding, however, creates caps, closures, and more complex packaging elements.
Medical Industry
Injection molding is critical for the medical industry due to its ability to produce precise and complex parts like syringes, casings for medical devices, and other equipment. Blow molding can be used for some medical containers but plays a lesser role than injection molding.
Factors to Consider
Product Shape and Size
If your product needs to be hollow, such as a bottle or container, blow molding is the go-to choice. For solid parts or detailed designs, injection molding is typically more appropriate.
Material Selection
Some materials are better suited for one process over the other. Lightweight materials like polyethylene work well in blow molding, while stronger materials like ABS are preferred for injection molding.
Production Volume and Cost
For high production volumes of hollow products, blow molding is more cost-effective. However, for parts that require fine details and structural strength, injection molding provides better value, especially for larger production runs.
One misconception is that blow molding and injection molding are interchangeable. In reality, they serve distinct purposes and cannot be swapped without sacrificing product quality. Another myth is that injection molding is always more expensive, but it can actually be more cost-effective for large-scale projects requiring complex parts.
Blow molding and injection molding each offer unique benefits and applications. Choosing between the two depends on your product’s shape, size, material, and desired volume. While blow molding is ideal for creating hollow, lightweight products, injection molding excels in making durable, intricate parts. Understanding these differences will help you select the right process for your next project.
This is the first one.